Understanding everything about how VR headsets work
Virtual reality (VR) is defined as a technology that produces a three-dimensional simulation of an environment. The surroundings can then be walked through, creating a sense of immersion. Thus, these devices make the dream of new horizons accessible with a complete and captivating sensory experience. The potential of VR is constantly evolving, so much so that it is disrupting our daily lives as its fields of application multiply. What principles are behind virtual reality headset? In this article we explain the origin of 3D glasses, how they work and what they are used for.
What is virtual reality?
A dream hard to reach
The ancestor of virtual reality is attributed to Morton Heilig and his Sensorama machine, which invites the user to call upon several senses. This device, presented in 1962, resembles an arcade terminal, had a wind tunnel to simulate the wind and even a perfume diffuser. Nevertheless, the project failed to convince and it was not until the early 1980s that the first virtual reality headsets as we know them appeared.
A space technology
NASA produced the VIEW (Virtual Interface Environment Workstation) system, which provided a vertical viewing angle of 120° thanks to two 2.7 inch LCD screens. The helmet is then complemented by a voice recognition system and Dataglove accessories from VPL research. The army was also a pioneer in the development of VR, notably with the creation of the Super Cockpit or VCASS (Visually Coupled Airborne Systems Simulator). This device, nicknamed Darth Vader because of its shape, is used to simplify the piloting of combat aircraft.
The golden age of virtual reality
The 1990s saw the commercialisation of numerous headsets with unfinished technologies, leading to the disappointment of a public with feverish expectations. The 2010s will open a new era for VR with the explosion of the video game field and the technological revolutions that led to the Oculus Rift, the Virtuix Omni, the Google Cardboard or the Samsung Gear VR. Since then, the range of products on the market has grown and the fields of application of virtual reality are becoming increasingly diverse.
A high-performance sensory device
Reality is rooted in our senses. A scene is made up of an image, an associated sound, the touch of the materials around, but also the surrounding smell. To immerse the user, virtual reality should deliver a realistic transcription of all these parameters.
An image alone cannot convey the everyday experience, which is why VR headsets are combined with other devices, such as audio headsets. Its fundamental purpose is to make our senses believe that what we are experiencing is not fictitious, but part of a reality. The whole point of virtual reality lies in this illusion. The more senses the device deceives, the more real the experience will seem to our brain.
A stable and reactive system
The feeling of immersion emerges when the quantity and quality of the data received by the user coincide. The stability of the system guarantees a convincing experience. Therefore, headsets should have a minimum of latency, i.e. a low response time between the system and the action. Indeed, if the device jerks or does not follow the movements correctly, the user will easily come out of the immersion.
A believable 3D environment
Video games and animated films have accustomed us to 3D. For immersion to work, the associated environment must be as credible as possible. Most of the time, these are created on computers using specific software such as Unreal Engine or Unity.
Unlike augmented reality, which inserts virtual information into an existing landscape, virtual reality is based on virtual technology. In order to be persuasive, the various elements presented must react according to the user’s position and orientation. The 3D sound feedback plays a fundamental role in that matter, since it allows objects to be located in space.
How do virtual glasses work?
VR headsets usually consist of several components:
- a screen to project images;
- lenses to distance the user from the screen;
- a computer, connected to the headset, to run the simulation (optional depending on the model).
The virtual glasses are generally connected to the computer by a USB cable and an HDMI cable, the first being used for communication with the PC, the second transmitting the image to the helmet. They also have a power cable. However, this traditional configuration is becoming simpler. The virtual headset is now independent of the computer and becomes autonomous. In this way, the device becomes more mobile and practical to use.
VR glasses work by stereoscopy, a technique that allows the brain to distinguish the relief. How does it proceed? It combines two flat images perceived by each eye into one. These stereoscopic images, generated by the computer or the headset, are projected onto two lenses in front of each eye. Motion tracking then takes place so that the user’s head movements are reflected on the screen.
In addition, the field of vision is close to that of a human, i.e. 180°. To ensure perfect immersion, the helmet must display a minimum of 90 frames per second. However, the higher the number of frames per second, the more powerful the device will need to be.
However, the power needed to ensure a well functioning system grows as the number of frames increases.
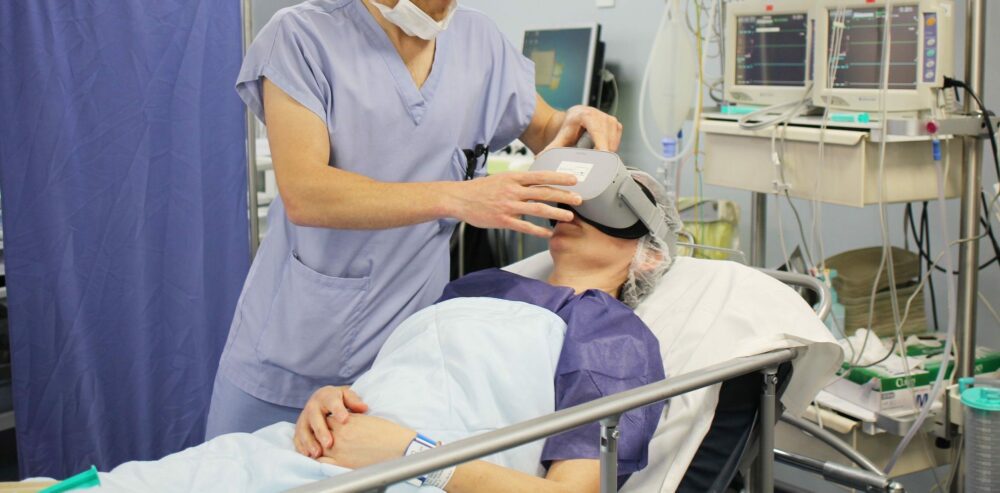
How to put on a VR headset?
After presenting all the technical requirements, let’s talk about one last parameter that is essential for using a 3D headset: comfort. For the magic to happen in front of your eyes, the glasses must fit your face perfectly. The less you feel the device, the more positive the immersion will be. To put on a VR helmet, simply slip it on and adjust the size to your liking.
It is best to put on the headset in an open space so that you don’t encounter any obstacles during your experience. As a general rule, 3 metres in length and 1.9 metres in width are sufficient. If you experience eye strain or nausea, remove the virtual glasses immediately.
What are the areas of application of virtual glasses?
1. Adopting 3D glasses in the education sector
Education is not the first sector that comes to mind when people think of virtual reality. However, it has considerable benefits for learning. VR is of great interest because of its playfulness and interactivity. Where subjects seem abstract or take place in the past, simulations convey a sense of proximity.
Numerous applications have been developed in this respect, such as Google Earth VR, which offers a complete tour of the planet, or Unimersiv, which immerses us in historical reconstructions of Ancient Rome or the Acropolis in Athens. Virtual reality offers new educational possibilities.
2. Escape with a virtual helmet to travel
VR headsets respond to the need for immediacy by offering a quick and deep disconnection. Not only do they allow you to cross borders in a matter of seconds, they also generate extraordinary experiences for everyone.
Climbing the highest peaks, diving miles deep, flying over a gigantic desert, nothing is impossible. National Geographic VR is a fine example of this type of production.
3. Immerse yourself in video games with a VR headset
Video games are the most prolific field for virtual reality. The range of games is growing every year and with it the 3D devices market. With the emergence of stand-alone VR headsets, the number of users is increasing.
The principle is to immerse the player in the heart of a quest or a mission that he or she must accomplish. This can be as simple as starting a revolution in Half-Life: Alyx or surviving in the post-apocalyptic world of Fallout. Each game pushes the boundaries of technology by innovating in the scenarios and the visuals areas.
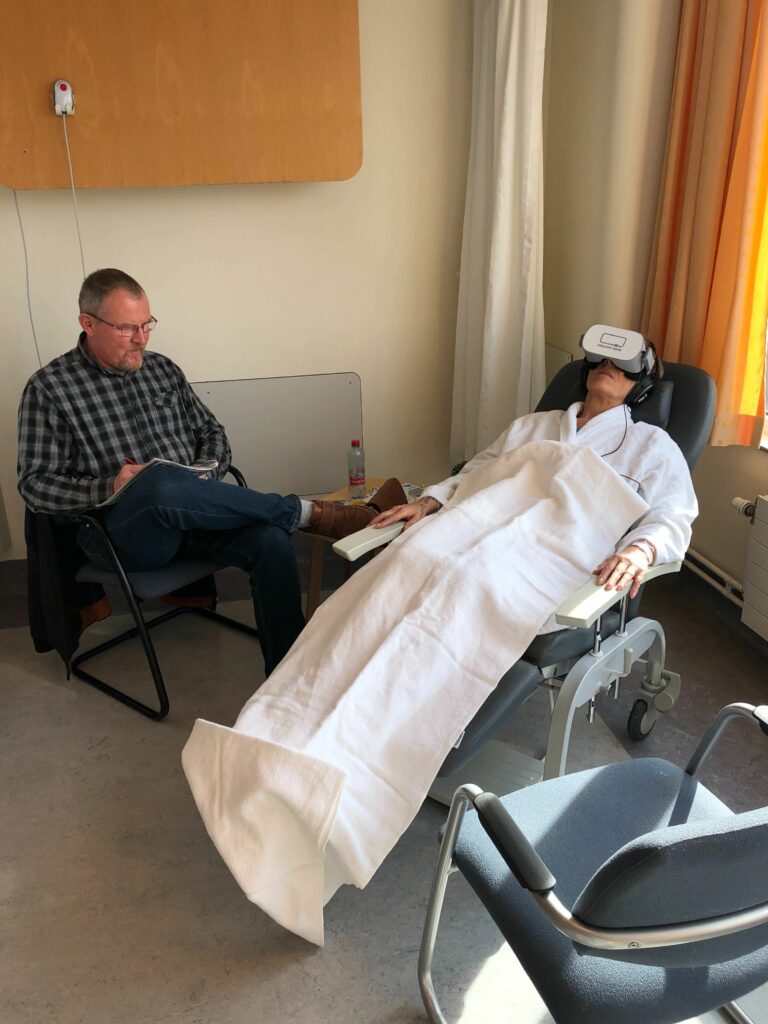
4. Using a therapeutic virtual reality headset
Twenty years of research and dozens of international scientific publications later, the opinion is unanimous: therapeutic virtual reality has an analgesic and anxiolytic effect. This non-medicinal solution delivers a deep soothing effect and has a multitude of applications such as
- relaxing during a dental consultation;
- accompanying patients in palliative care;
- recovering more quickly after a surgery;
- improving the chances of a successful IVF puncture;
- coping with chronic pain.
Of course, this list is by no means exhaustive. We invite you to discover the use cases of the Healthy Mind device to understand the full potential of this technology in the medical sector.
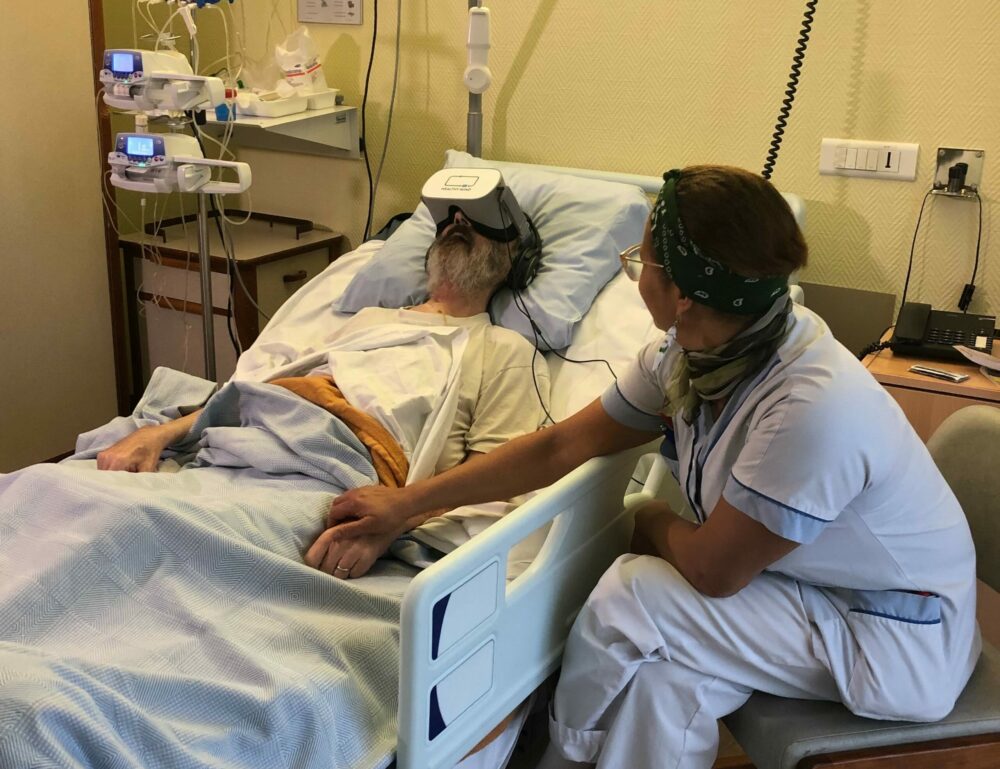
How does Healthy Mind use virtual reality for medical purposes?
Our therapeutic virtual reality solution consists of an application, Healthy Mind VR, on a stand-alone headset, which delivers access to natural virtual environments: a Zen garden, a snowy mountain, a forest walk, a sunny beach, an underwater world and a sunny mountain. These have been specifically designed to reduce patients’ pain and anxiety.
The 3D landscapes are mixed with advanced psychology principles such as medical hypnosis, music therapy and breathing techniques to bring the patient into a state of cardiac coherence. Each environment is associated with a specific hypnotic support. Sessions last from 5 to 80 minutes and the hypnotic output can be triggered at any time. The practitioner has a tablet, Healthy Mind Control, to set up, control and monitor the immersion.
We chose the Pico G2 4K E headset for its graphic quality (4K resolution) and for its autonomy of 2.5 hours. We accompanied these virtual glasses with Bose Quiet Comfort 35 II headphones with noise reduction for comfort and total immersion. All the equipment can be easily stored in a backpack for transport.
We would be delighted to answer any questions you may have about our device, so feel free to contact us and ask for a demonstration.