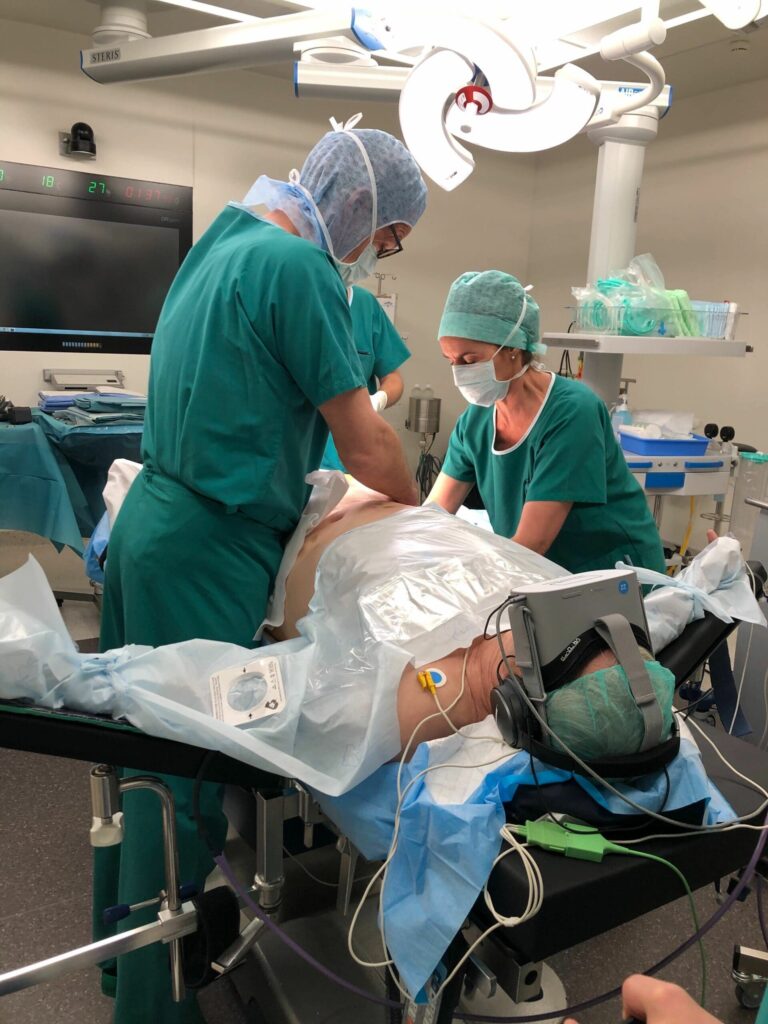
Anesthesiology
Indications
BEFORE A PROCEDURE
- To reduce the patient's (and the accompanying person's) pre-operative anxiety
- To use only non-pharmacological anxiolysis or to reduce the consumption of associated anxiolytics
- To favour, if possible, a loco-regional rather than a general anaesthesia
- To minimise the potential negative effects of the forthcoming operation
DURING A PROCEDURE
- Central and peripheral blocks
- Acts under local anaesthesia
- Orthopedic surgery: hand, knee, hip
- Oncology: lumpectomy, mastectomy, prostatectomy
- Port, catheter, puncture, injection, angioplasty, varicose veins, perfusion, dressings
- Bronchial endoscopy, digestive endoscopy, ureteroscopy, lithotripsy
AFTER A PROCEDURE
- To reduce the patient's anxiety and pain after surgery
- To accelerate the patient's recovery and help prevent the onset of chronic pain
- To reduce the intensity of symptoms encountered in the intensive care unit (discomfort, pain, anxiety, insomnia etc.)
Clinical studies with our solution

| -50% | +24 |
| DISCOMFORT | ANI SCORE |
Improving the discomfort of critically ill patients with electronic relaxation devices, Critical Care 2022.
L. Merliot‐Gailhoustet, et al.
Results : HEALTHY-MIND© was associated with a significant decrease in global discomfort, the primary endpoint (median NRS=4[2-6] vs. 2[0-5]; p=0.01, mixed model), accompanied by a significant decrease in stress response (increase in ANI, secondary endpoint; p<0.01). HEALTHY-MIND© was also associated with a reduction in pain intensity and anxiety by 0.8 points compared to standard relaxation (p=0.001 and 0.004, respectively). N=60


| -33% | -83% |
| ANXIETY | MORPHINE |
Effectiveness of virtual reality in reducing anxiety and pain during paediatric idiopathic scoliosis surgery, SFAR 2021
R. Assener, et al.
Customer feedback on video
Customer feedback
on video
Testimonies