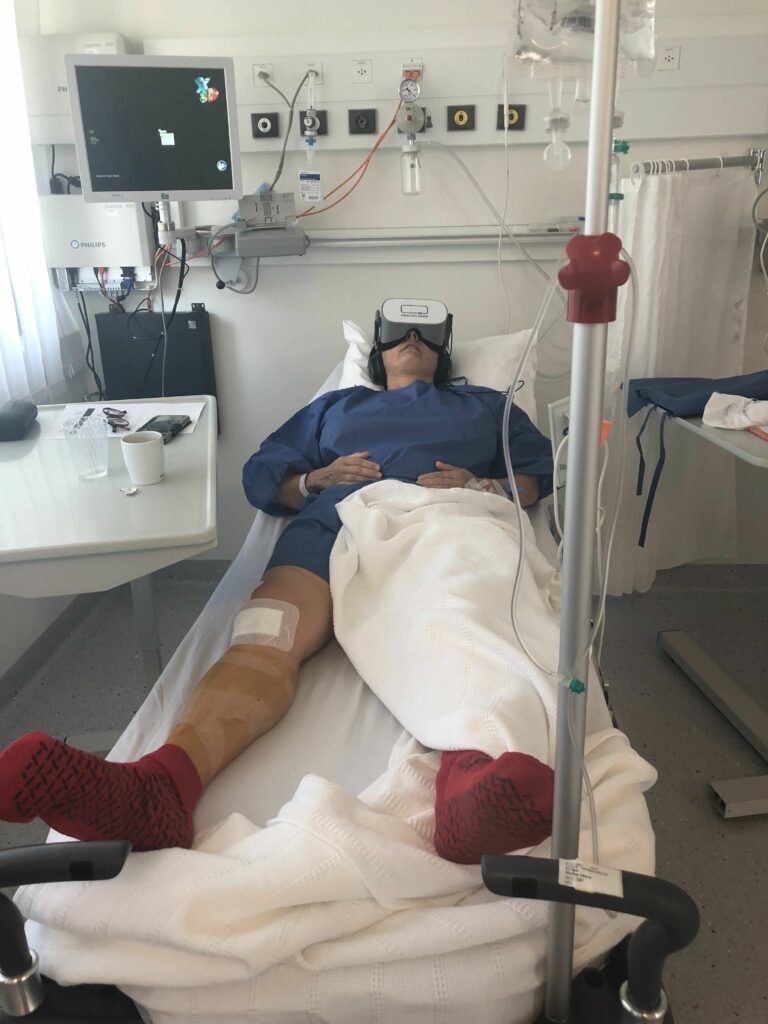
Wound treatment
Indications
- Examination, wound treatment and dressing changes
- Physical therapy for burn victims
- Reducing the use of opioids in care
- For children and adults

Clinical studies
Clinical studies

| -38% |
|---|
| OPIOIDS |
Immersive virtual reality to reduce opioid use during painful wound care procedures in adults, Journal of Burn Care & Research, 2018
McSherry T., et al.
Results: The amount of opioids administered before each of the 2 wound procedures was similar with and without IVR. Total opioid administration during dressing procedures with IVR was significantly lower than when no IVR was used, 17.9±6.0 and 29.2±4.5 mcg/kg fentanyl, respectively (t=˗2.7; df=14; p=0.02) N=18
OF PAIN |
Immersive virtual reality as analgesia during dressing changes for hospitalized children and adolescents with burns, Children (Basel.), 2020
Lauwens Y., et al.
Results: This meta-analysis of 4 scientific studies concluded that there was a significant size effect demonstrating the effectiveness of VR in reducing pain during burn care compared to conventional care. N=104