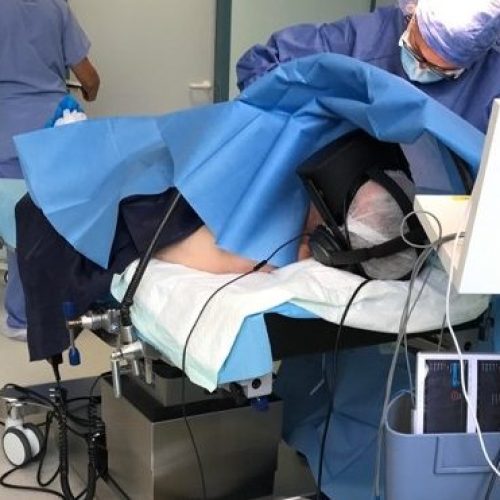
Surgery
Indications
BEFORE A PROCEDURE
- To reduce the patient's (and the accompanying person's) pre-operative anxiety
- To use only non-pharmacological anxiolysis or to reduce the consumption of associated anxiolytics
- To favour, if possible, a loco-regional rather than a general anaesthesia
- To minimise the potential negative effects of the forthcoming operation
DURING A PROCEDURE
- Surgery under loco-regional anaesthesia
- Thoracic and orthopaedic hand, knee and hip surgery
- Aesthetic, plastic and reconstructive surgery
- Vascular surgery and percutaneous aortic valve replacement
- Digestive surgery
AFTER A PROCEDURE
- To reduce the patient's anxiety and pain after surgery
- To accelerate the patient's recovery and help prevent the onset of chronic pain
- To reduce the intensity of symptoms encountered in the intensive care unit (discomfort, pain, anxiety, insomnia etc.)
- To perform negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT)
Clinical studies with our solution
Clinical studies with our solution

| -33% | -83% |
| ANXIETY | MORPHINE |
Effectiveness of virtual reality in reducing anxiety and pain during paediatric idiopathic scoliosis surgery, SFAR 2021
R. Assener, et al.
Results: For the primary outcome: the median VAS for anxiety in children decreased after the use of virtual reality: 6 [1; 7] versus 4 [0; 5] in children, p = 0.01. This decrease in median VAS was maintained at D+1 and D+4 postoperatively at 1 [0; 2]. This decrease in median VAS was maintained at D+1 and D+4 postoperatively at 1 [0; 2]. Median morphine consumption was 0.21mg/kg/24h [0.02; 1.4] vs 1.2mg/kg/24h [0.02; 3.5] for the control group. N=43

| +20% | 96% |
| -8POINTS | WOULD DO |
| STAI-YA | IT AGAIN |
Investigating the impact of virtual reality on anxiety during dental avulsions under local anaesthesia, Thèse – Faculté de Médecine de Caen, 2022
Pr. H. Bénateu, et al.
Clinical studies
Clinical studies

| -46% | 353% |
| ANXIETY | AMUSEMENT |
Virtual reality improves patient experience during tourniquet-free hand surgery under broad spectrum local anaesthesia, Journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeon, 2019
E. Hoxhallari, et al.
Results: Anxiety and amusement scores were significantly different at each time point in virtual reality patients compared to non-virtual reality patients (p<0.04). The study separated the results during the injection, during the procedure and at the end of the procedure. Anxiety is one of the main reasons why patients are deterred from certain surgeries. N=41
Testimonies