All our use cases > Paediatrics
Paediatrics
Indications
- Painful procedure involving needles, venipunctures, lumbar punctures, perfusion
- Before and after surgery such as idiopathic scoliosis
- Reduction of parental anxiety
- Changing wound dressings, applying plaster
- Anxiety and pain management in paediatric intensive care units
- Pain and anxiety in pediatric palliative care
- Escape sessions during immobility
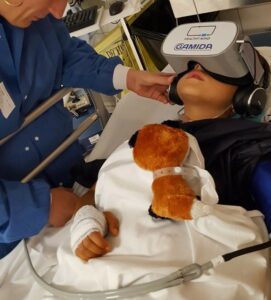
Clinical studies with our solution
Clinical studies with our solution


| -33% | -83% |
|---|---|
| ANXIETY | MORPHINE |
Effectiveness of virtual reality in reducing anxiety and pain during paediatric idiopathic scoliosis surgery, SFAR 2021.
R. Assener, et al.
Results: For the primary outcome: the median VAS of anxiety in children decreased after the use of virtual reality: 6 [1; 7] versus 4 [0; 5] in children, p = 0.01. This decrease in median VAS was maintained at D+1 and D+4 postoperatively at 1 [0; 2]. This decrease in median VAS was maintained at D+1 and D+4 postoperatively at 1 [0; 2]. Median morphine consumption was 0.21mg/kg/24h [0.02; 1.4] vs 1.2mg/kg/24h [0.02; 3.5] for the control group. N=43


| -57% |
|---|
| ANXIETY CHILDREN & PARENTS |
Evaluation of a virtual reality headset in the prevention of peri-operative anxiety in children, SFAR 2019.
L. Marsac, et al.
Results: Children’s and parents’ anxiety was lower after the children’s immersion in Virtual Reality: 7[5-10] vs. 3[2-7] in children, p=0.001 and 7[2-10] vs. 3[2-6) in parents, p=0.01. No patients showed agitation at induction or in the PACU. The concomitant effect on parental anxiety is a major beneficial effect because of the strong connection between children’s and parents’ anxiety. N=15