Internal Medicine
Indications
POSSIBLE INTERVENTIONS
- Conditions requiring hospitalization
- Inflammatory autoimmune diseases
- Genetic diseases diagnosed in adulthood or evolving since childhood
- Immunodepressive diseases...
BEFORE/DURING/AFTER INTERVENTION
- To reduce the patient's (and the accompanying person's) pre-operative anxiety
- To use only non-pharmacological anxiolysis or to reduce the consumption of associated anxiolytics
- To favour, if possible, a loco-regional rather than a general anaesthesia
- To minimise the potential negative effects of the upcoming procedure
- To reduce the patient's post-procedure anxiety and pain
- To accelerate the patient's recovery and help prevent the onset of chronic pain
- To reduce the intensity of symptoms encountered in the intensive care unit (discomfort, pain, anxiety, insomnia etc.)
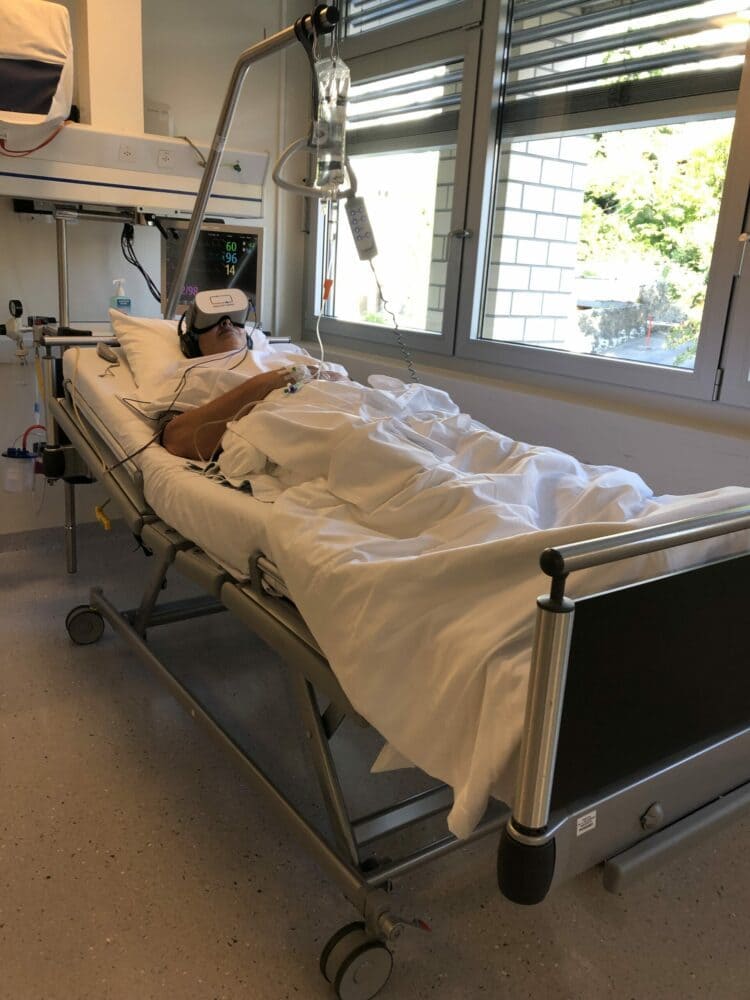
Clinical study with our solution
Clinical study with our solution

| -50% | +24 |
|---|---|
| DISCOMFORT | ANI SCORE |
Effectiveness of virtual reality in reducing anxiety and pain during paediatric idiopathic scoliosis surgery, SFAR 2021.
L. Merliot‐Gailhoustet, et al.
Results : HEALTHY-MIND© was associated with a significant decrease in global discomfort, the primary endpoint (median NRS=4[2-6] vs. 2[0-5]; p=0.01, mixed model), accompanied by a significant decrease in stress response (increase in ANI, secondary endpoint; p<0.01). HEALTHY-MIND© was also associated with a reduction in pain intensity and anxiety by 0.8 points compared to standard relaxation (p=0.001 and 0.004, respectively). N=60
Clinical study
Clinical study

| -3 points |
|---|
| SEVERE PAIN |
Virtual reality for pain management in hospital patients, Public Library of Science, 2019
B. Spiegel, et al.
Results: Shapiro-Wilk test used (p=0.19). A T-test showed that the mean difference was significant in favour of VR (p<0.04). Restricting to the subgroup of patients with the most severe baseline pain (≥7 points; N=54), the effect of VR was more pronounced compared to control (-3.04, SD 3.75 vs -0.93 points, SD 2.16; P=0.02). Age was also a significant predictor in this multivariable model, with each additional 10 years of age predicting a 0.6 point reduction in pain (p=0.001). N=120