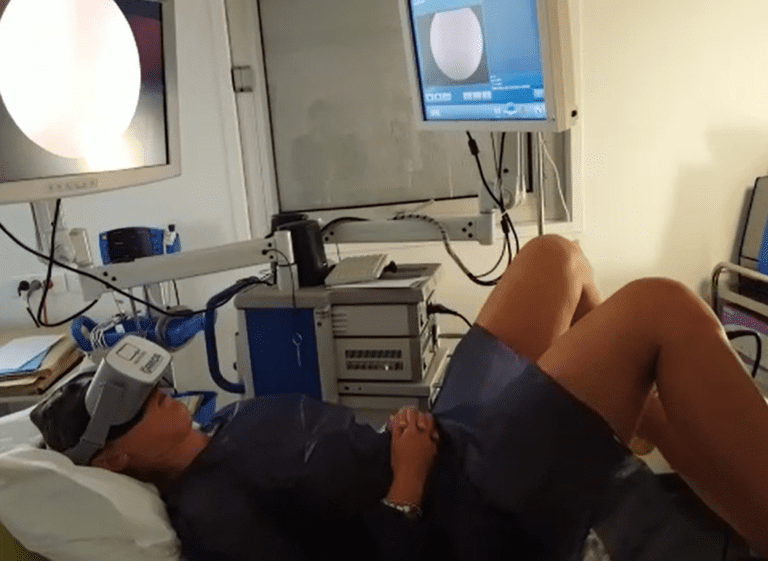
Gynecology and maternity
Gynecology
and maternity
Indications
- Hysteroscopy
- follicle puncture to collect oocytes, embryo transfer
- IUD insertion
- Voluntary termination of pregnancy (IVG)
- Epidural placement for labour
- During labor phase
Clinical studies
Clinical studies

| -28% | -38% | -38% |
|---|---|---|
| SEVERE PAIN | PAIN AVERAGE | ANGST |
Virtual reality for acute pain in ambulatory hysteroscopy, BJOG an international Journal for Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 2020
Deo N., et al.
Results: Compared to standard care, the virtual reality intervention had a significant effect in reducing the most severe pain with a difference of 2.2 (28% reduction, score 7.85 vs. 5.65, 95% CI 3.79-3.79, p=0. 011, Cohen’s d 0. 82), average pain with a difference of 2.3 (38% reduction, score 6.0 vs. 3.7, 95% CI 0.61-3.99, p=0.009, Cohen’s d 0.81), and anxiety with a difference of 2.15 (39% reduction, scores 5.45 vs. 3.3, 95% CI 0.38-3.92, p=0.024, Cohen’s d 0.73). N=48

| -36% | -38% |
| ANXIETY | DEPRESSION |
The use of pre-operative virtual reality to reduce anxiety in women undergoing gynaecological procedures, BMC Anesthesiology, 2020
Chan J. J. I, et al.
Results: The analysis revealed that HADS anxiety scores were significantly reduced from 7.2 ± 3.3 pre-intervention to 4.6 ± 3.0 post-intervention (p < 0.0001). In addition, HADS depression scores were significantly reduced from 4.7 ± 3.3 pre-intervention to 2.9 ± 2.5 post-intervention (p < 0.0001). 82% of patients rated the VR procedure as “good” or “excellent”. N=108

| -31% | -38% |
|---|---|
| UNPLEASANT PAIN | WORST PAIN INTENSITY |
Virtual reality analgesia during labour in pregnant women, Anesthesia & Analgesia, 2019
Frey D. P., et al.
Results: NRS scores for the primary outcome of worst pain intensity (sensory pain) were significantly lower in the VR condition (slope estimate -1.5 [95% CI, -0.8 to -2.2]). NRS scores for the secondary outcomes of affective pain (slope estimate -2.5 [95% CI, -1.6 to -3.3]), cognitive pain (slope estimate -3.1 [95% CI, -2.4 to -3.8]) were also significantly lower in the VR condition. NRS scores for anxiety were also lower in the VR condition than in the non-VR condition (slope estimate -1.5 [95% CI, -0.8 to -2.3] and standardised mean difference -0.7). N=28