Scientific study: Feasibility of combining spatial computing and artificial intelligence in cases of anxiety and depression
Mental illness and psychological disorders affect nearly one-fifth of the population, including 13 million French citizens according to data from the World Health Organization (WHO). At a time when mental health issues are on the rise and access to care is becoming more complex, new technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to meet the growing needs of patients. How can these digital tools provide personalized therapeutic support? Research developed by the Cedars-Sinai Medical Center sheds light on the potential of an alliance between virtual reality and artificial intelligence. The quotes in this article are taken from the references cited in the study conducted by Spiegel, B.M.R., Liran, O., Clark, A., et al. Feasibility of combining spatial computing and AI for mental health support in anxiety and depression.
The context of the study: challenges and innovations in mental health
A growing need for psychotherapeutic care
Over the years, the prevalence of mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, has steadily increased. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated this trend by imposing social isolation, generating economic instability and intensifying feelings of loneliness.
According to Santé publique France’s 2021 health barometer, the prevalence of depressive episodes experienced an unprecedented acceleration between 2017 and 2021, rising from 9.8% to 13.3%. To track the evolution of these behaviors, Santé publique France organised a CoviPrev survey in December 2022. The results remain alarming, with one-third of respondents presenting an anxious or depressive state.
Against this backdrop, the need for broader access to psychotherapeutic care is particularly felt. However, many obstacles persist:
- an insufficient number of professionals;
- often high consultation costs;
- the stigma associated with seeking psychological help.
This situation creates an urgent need for innovation to make therapies more accessible and better adapted to individual needs.
The challenge of personalising virtual reality (VR) experiences
Virtual reality offers an innovative way to approach therapy by creating immersive environments that soothe the mind and facilitate personal reflection. The usual barriers decrease thanks to the playful aspect of the device.
Yet, personalisation remains a true challenge: traditional VR experiences are generally based on pre-recorded scenarios, thereby limiting their ability to adapt to individual journeys and expectations.
The integration of artificial intelligence paves the way for interactive and customisable experiences in real time. In this perspective, the XAIA program combines VR and AI to offer tailored psychological support. The study investigates the effectiveness of a therapeutic alliance through a virtual avatar to reduce various biopsychosocial issues.

The study’s method: a platform combining VR and AI for psychological support
The XAIA program (eXtended-reality Artificial Intelligence Assistant) is an innovation developed by the Cedars-Sinai team. This system combines the power of virtual reality with the learning capabilities of an AI based on GPT-4 to create an immersive and interactive therapeutic experience. The system’s development involved iterative testing with therapists enacting clinical scenarios to refine communication.
At launch, the user can choose from nine nature-inspired environments (forests, beaches, celestial landscapes, etc.). This atmosphere establishes a relaxing setting conducive to introspection. A therapeutic avatar named XAIA, designed to initiate and guide the psychological support session, then welcomes the user.
The interaction takes place through sophisticated technology: audio is converted into text by voice recognition systems, analysed by GPT-4 which generates appropriate responses, and then retransmitted in vocal form via a text-to-speech system. The conversations are processed via a server that complies with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) standards.
An appropriateness classifier ensures that the responses remain in line with therapeutic and safety standards. This processing chain simulates an empathetic and personalised conversation, incorporating proven techniques from cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT).
The results: promising perspectives for acceptability and safety
Researchers tested XAIA with 14 participants exhibiting mild to moderate anxiety or depression. The interviews revealed that most of them found the experience useful, safe, and calming.
XAIA successfully applied key psychotherapeutic techniques such as empathetic listening, validation of feelings, and reassurance. For example, when a user expressed feelings of rejection, XAIA responded:
“I’m sorry to hear that you felt so definitively rejected, especially while pursuing what is important to you. That must have been a difficult experience.”
Participants also experienced a sense of relaxation thanks to the immersive landscapes and soothing sounds of VR. Some mentioned preferring to interact with a non-judgmental AI, particularly those who were reluctant to consult a therapist in a traditional setting.
The combination of virtual reality and artificial intelligence represents a significant advance in the quest for innovative solutions to psychological support. XAIA paves the way for digital therapy that could broaden access to care, especially for isolated people or those living in areas where access to qualified professionals is limited.

Identified limitations in the therapeutic approach using VR with artificial intelligence
Despite promising results, the study also highlighted certain limitations. In some cases, XAIA asked too many questions—even repetitive ones—giving the impression of a superficial interaction. For example, when a user mentioned a job loss, the focus was on immediate coping strategies rather than a deeper exploration of the underlying emotions.
Additionally, some CBT techniques, such as cognitive restructuring or mindfulness exercises, were sometimes introduced without sufficient context, at the risk of destabilising users who were unfamiliar with these approaches.
Finally, despite the technological sophistication, several participants expressed a preference for human interaction, underlining the importance of direct communication to establish a genuine emotional connection and personalised follow-up.
The researchers are considering several avenues for improvement to strengthen the effectiveness of their approach:
- enhancing virtual environments with dynamic elements (lighting, water movement, etc.);
- increasing the personalisation of interactions based on the specific needs of users;
- integrating advanced features such as the ability to choose different voice options or adjust the length of sessions.
Longitudinal studies will be essential to measure the clinical impact of these innovations on reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Is it possible to integrate VR into therapeutic support? To explore this question, we interviewed the personal and professional development coaching firm Agissons Ensemble about their specific use of the Healthy Mind device.
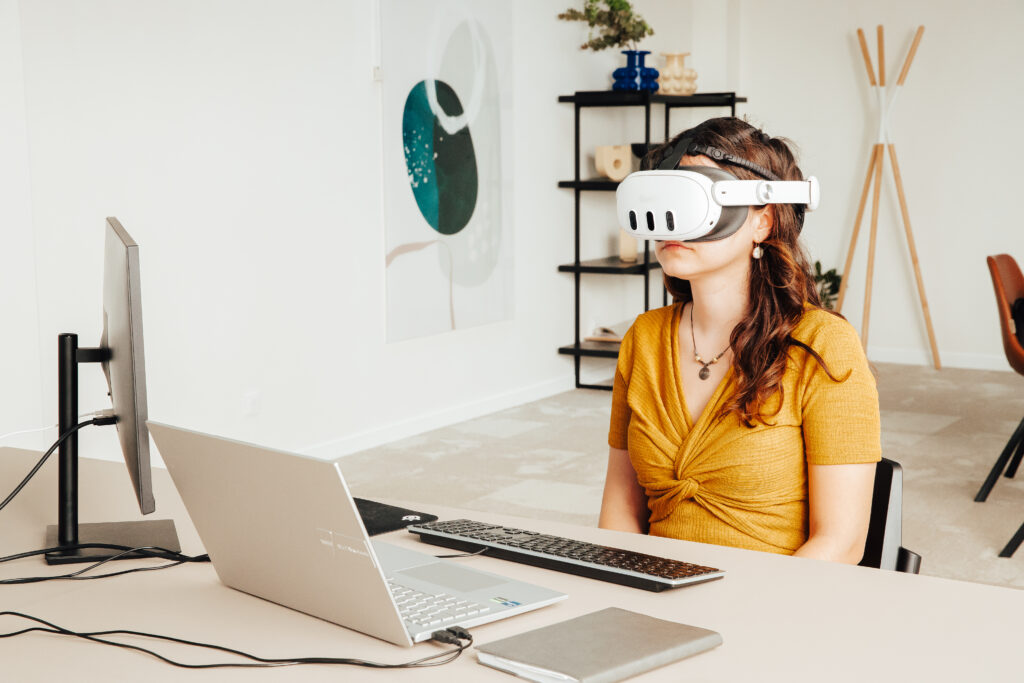

Neuromind device: an innovative neurofeedback solution based on emotional measurement
For several years now, the Healthy Mind research team has been working on a product capable of supporting patients with chronic conditions such as depression. The Neuromind device thus combines encephalography (EEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and eye tracking with virtual reality immersion. Thanks to a headset integrating EEG electrodes, brain activity is measured in order to capture the cognitive patterns at work.
The algorithms we developed detect and classify the data according to the proprietary biomarkers of attention and emotion. Beyond interpreting the emotional state, Neuromind works alongside the virtual reality headset to assess what the 3D environment provides to the user. After defining a target state—relaxation, for example—the immersive experience evolves until the user reaches it.
The qualitative study on the XAIA program illustrates the capacity of new technologies to meet the challenges of mental health. While human interaction remains highly valued by many patients seeking empathy, artificial intelligence offers a useful and accessible alternative in a context where the demand for psychological support continues to grow. In this sense, virtual reality based on neurofeedback shows the potential to transform mental health treatments. If you would like to experience the benefits of our devices for yourself, we would be delighted to offer you a demonstration.
Sources :
- Spiegel, B.M.R., Liran, O., Clark, A. et al. Feasibility of combining spatial computing and AI for mental health support in anxiety and depression. npj Digit. Med. 7, 22 (2024);
- Press release from the Ministry of Health and Prevention, Summary of the assessment of the roadmap, mental health and psychiatry, March 2023.