Scientific study: supporting behavioral change in patient undergoing elective surgery with digital and mobile technologies
Today, connected devices have become an integral part of our daily lives, with innovative digital technologies gradually infiltrating various fields, including healthcare. While artificial intelligence has already proven its worth in medical learning and diagnosis, new applications are emerging to assist patients throughout the perioperative journey. Could these engaging and appreciated tools serve as support to induce positive behavioral changes during non-urgent surgeries? A literature review conducted in October 2019 aims to shed light on this significant topic. Quotations in this article are extracted from references cited in the meta-analysis by Anna Robinson et al., Digital and Mobile Technologies to Promote Physical Health Behavior Change and Provide Psychological Support for Patients Undergoing Elective Surgery: Meta-Ethnography and Systematic Review.
The context of the study: digital tools and their role in elective surgery’s care pathway
Factors influencing recovery after elective surgery
Physical and psychological preparation before surgery influences postoperative outcomes. Unsurprisingly, increased physical activity, improved nutrition and smoking cessation lead to reduced complications, greater treatment tolerance, and long-term disease prevention.
However, despite these recognised effects, the practical application varies among patients. Knowing the theory doesn’t necessarily facilitate implementation. Without intervention or support, motivation tends to fade. How then can the motivation of each individual be maintained to uphold these resolutions?
Enhancing postoperative recovery success using digital and mobile technology
In response to the demand for support, healthcare professionals organize numerous physical and mental health interventions during the care journey. However, these approaches require resources that the healthcare sector sometimes struggles to gather.
Additionally, geographical isolation, travel costs and time constraints also act as barriers to profound lifestyle changes. Integrating digital technologies into the perioperative process, such as a therapeutic virtual reality solution to reduce pain and anxiety, can provide guidance and support to increase patients’ success rates.

The study method: meta-synthesis
Meta-synthesis involves cross-referencing multiple results from existing qualitative research on a specific research question. However, this approach goes beyond data compilation. Meta-synthesis includes an interpretation phase to develop or complete a theory. The first to mention this innovation were Noblit and Hare in 1988, who referred to it as the meta-ethnographic method.
In the context of Anne Robinson et al. study, this approach examines the effectiveness of digital technologies in helping patients undergoing elective surgery to change their behaviour. To this end, six databases, as well as articles from Google Scholar, were used as references. The focus was set on bariatric, cancer and orthopaedic surgery. Acute, unplanned interventions and emergency trauma procedures were excluded from the analysis.
No restrictions were imposed based on participants’ gender, ethnicity or nationality, or on the time frame. The study also excluded research lacking digital intervention in the behavioural change achieved.
The 18 selected studies were published between 2013 and 2019 in eight different countries. Based on these data, the research team selected four key themes to assess the relevance of digital and mobile technologies in supporting elective surgery patients.

The results of the study: the 4 axes for assessing the effectiveness of digital and mobile technologies in supporting postoperative recovery
1. Providing motivational support
Digital and mobile health technologies reinforce self-awareness. Thanks to activity trackers such as smartwatches, patients can keep a constant eye on their sedentary lifestyle. This enables them to initiate positive changes in their behaviour.
In addition, functions such as setting goals and performance feedback provide a sense of control and accomplishment:
“it’s very easy to know whether you’re doing well or not.”
Kokts-Porietis RL et al. Breast cancer survivors’ perspectives on a home-based physical activity intervention utilizing wearable technology. Support Care Cancer.
The accessibility offered by digital technologies is particularly reassuring for isolated patients who, for lack of means or time, are unable to travel to care centers:
“I really like it (telerehabilitation). I thought it was fantastic… you know, just not having to travel when you’re in pain.”
Kairy D et al. The patient’s perspective of in-home telerehabilitation physiotherapy services following total knee arthroplasty. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
However, reminders must not transform into pressure, judgement or fear of failure to be fully effective.
2. Taking an interest in patient engagement
The use of digital technology must be user-friendly to seamlessly integrate into patients’ daily lives. Complex apprehension of the tool hinders its use:
“For the most part, I don’t wear it because it doesn’t interact easily with my computer… What’s the point?”
Rosenberg D et al. Acceptability of Fitbit for physical activity tracking within clinical care among men with prostate cancer. AMIA Annu Symp Proc.
Complex interventions reduce the user’s enjoyment, which runs counter to the aim of the tools to fit seamlessly into everyday life. On the other hand, portability, like comfort, is a parameter that influences user engagement. With this in mind, our therapeutic virtual reality solution developed at Healthy Mind offers a compact, wireless, off-network device that adapts to movement and imposes as few constraints as possible.
Another parameter highlighted in the studies concerns the reliability of the technologies. Inaccurate information will inevitably reduce confidence in the device:
“It seemed to record less activity than I felt I was actually doing because it only measured steps, and I was doing more than steps. I was lifting things. I bent over. I twisted. I was doing all sorts of other things.”
Rosenberg D et al. Acceptability of Fitbit for physical activity tracking within clinical care among men with prostate cancer. AMIA Annu Symp Proc.

3. Facilitating peer networking
Digital technologies enable rapid and personalised feedback, satisfying patients’ information needs more efficiently. Using a platform such as an online forum with healthcare professionals provides evidence-based advice, ensuring greater safety and trust.
Beyond informational support, digital and mobile health technologies also offer emotional support for patients. Communicating with others who have been through or are going through the same experience helps to overcome feelings of loneliness and improve mental well-being:
“You know you’re not alone, but when your feelings are validated simply by reading someone’s story, it changes everything.”
Alberts NM et al. Patient and provider perceptions of internet-delivered cognitive behavior therapy for recent cancer survivors. Support Care Cancer.
Nevertheless, the attractiveness of connectivity should not entirely replace traditional face-to-face appointments. While a continuous presence behind a screen is reassuring, a physical presence allows for expressions of empathy that are crucial for patients’ mental comfort.
For this reason, we were keen to maintain constant communication in our Healthy Mind therapeutic virtual reality solution, with exchanges via messages or microphone. As a result, patients are never isolated, but in constant interaction with their carers during procedures.
4. Meeting individual patient needs
Each procedure, patient and illness is unique. For this reason, the integration of a digital and mobile device into the care pathway is assessed for each individual case, with specific levels of difficulty:
“Anyone with any disease can use this programme, which is beneficial, but it could be more beneficial […] if it were more tailored to the type of cancer or disease you have, your lifestyle and your fitness goals.”
Puszkiewicz P et al. Assessment of cancer survivors’ experiences of using a publicly available physical activity mobile application. JMIR Cancer.
Morevor, it seems essential to introduce the tools, empower and educate about the benefits of health behaviour changes at the right time. For example, in the case of cancer treatment, access to information at the time of diagnosis rather than at the time when the side effects of chemotherapy are occurring limits commitment to behaviour change.
The meta-analysis also highlighted the significance of certain graphic elements, such as the negative connotations of the colour pink for cancer patients, and the tone of the messages conveyed.
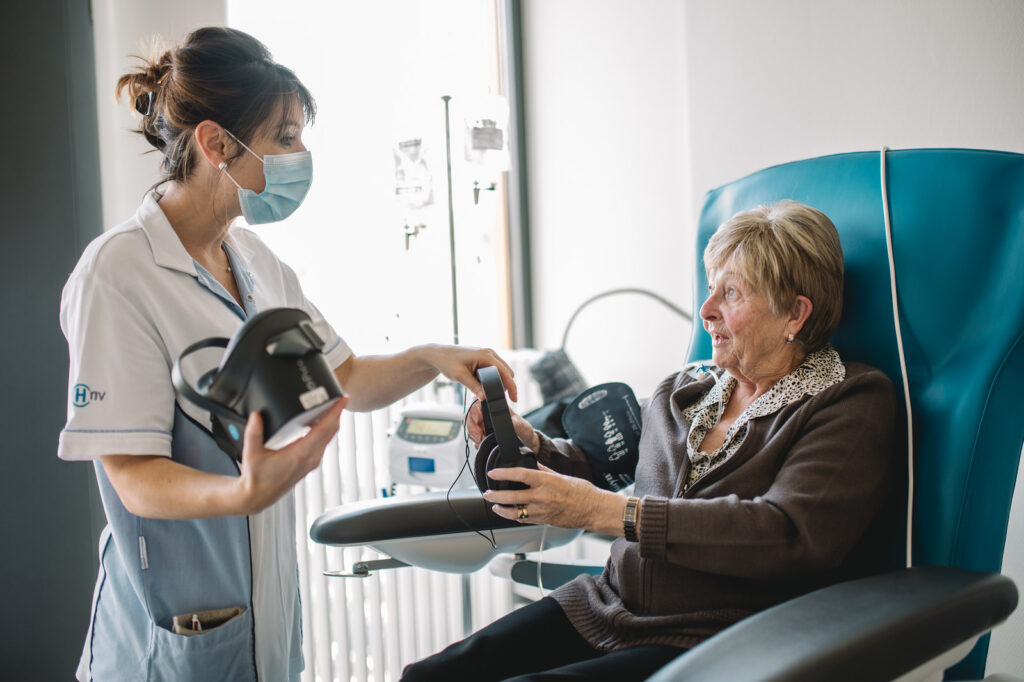

Healthy Mind device: therapeutic virtual reality to improve patient rehabilitation
While physical activity and nutrition contribute to improved postoperative recovery, mental health is also a critical factor. Stress complicates interventions, sometimes leading to the administration of sedative medications to soothe patients. A measure that is sometimes not without consequences…
Therapeutic virtual reality offers a way of dealing with the burden of anxiety without the use of sedatives. A number of techniques, including diversion, hypnotic principles and sophrology, combine to provide a bubble of relaxation. Before, during or after an operation, the use of virtual reality helps to speed up recovery.
To keep the patient in a comfortable environment, the virtual experience is carefully scripted with input from our medical team of anaesthetists and hypnotherapists. All elements that could create a feeling of unease are pushed aside.
As well as being a gateway to relaxation, therapeutic virtual reality meets the challenge of user-friendliness. Wireless, off-network and deployable in two minutes, the headsets adapt to meet hospital requirements and patient expectations. Throughout the immersion, medical personnel can interact with users through text message or microphone, maintaining the essential link between patients and caregivers.
“Healthy Mind’s immersive virtual reality solution has its place in the therapeutic arsenal, particularly as a complement to pharmacological sedation techniques […]. The immersive quality of the visual and sound environment, its realism and its customisation make it a high-quality tool”.
Dr Christophe Rabuel, anaesthetist-resuscitator, Lariboisiere Hospital – APHP.
Digital and mobile technologies act as catalysts for adopting healthy behaviours. Positive reinforcement, activity monitoring, the ability to interact with healthcare professionals and other patients, as well as the possibility of personalized pathways all reinforce the patient’s willingness to change their habits. Tool accessibility also ensures better continuity of care, a fundamental aspect in the face of hospital saturation and medical desertification in certain areas. With this in mind, the Healthy Mind device aims to reduce patients’ anxiety and pain by using relaxing and distracting elements, while maintaining a customizable approach and ergonomic functionality. If you wish to witness the benefits of our environments firsthand, we would be delighted to arrange a demonstration.
Source : Robinson A, Oksuz U, Slight R, Slight S, Husband A. Digital and Mobile Technologies to Promote Physical Health Behavior Change and Provide Psychological Support for Patients Undergoing Elective Surgery: Meta-Ethnography and Systematic Review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Dec 1;8(12):e19237. doi: 10.2196/19237. PMID: 33258787; PMCID: PMC7738263.